Fundamental:
Take a specific membrane material as an example. The membrane is fully wetted with a liquid that can be infiltrated into it. The infiltrating liquid becomes trapped in the pores of the membrane due to surface tension. A gradually increasing gas pressure is applied on one side of the membrane. When the gas pressure exceeds the surface tension of the liquid in a particular pore size, the liquid in that pore is pushed out by the gas. Since smaller pores have higher surface tension, more pressure is required to displace the liquid from them. As the pressure increases, the largest pores are opened first, allowing gas to pass through. Then, as the pressure continues to rise, the smaller pores are progressively opened, enabling gas to flow through until all the pores are clear and the permeability matches that of a dry film.
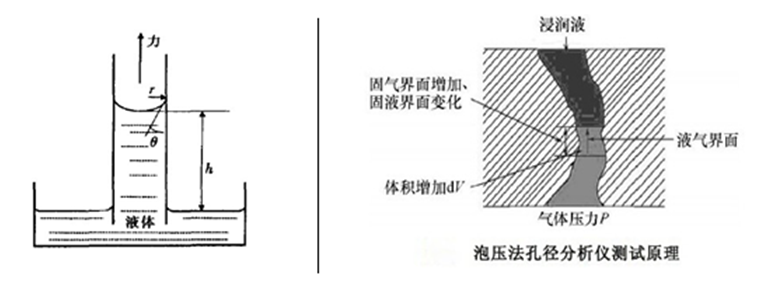
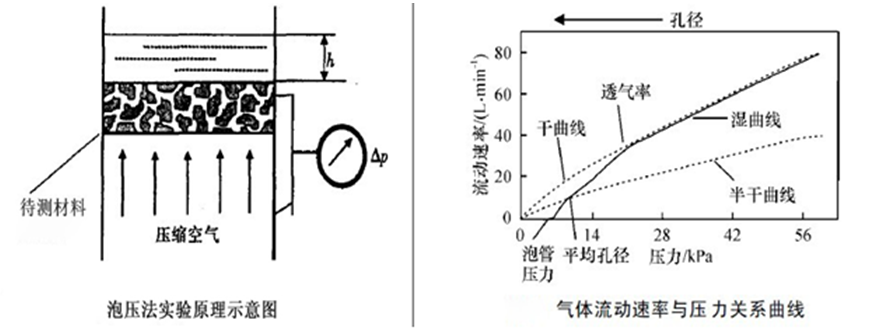
The pressure at which the first pore opens is called the bubble point pressure, and the corresponding pore size is known as the bubble point diameter. During this process, both pressure and flow rate are recorded in real time to generate a pressure-flow curve. This curve provides information about the pore sizes and the number of pores at each size. By testing the pressure-flow curve of a dry film, you can calculate key parameters such as pore size, average pore size, minimum pore size, pore size distribution, and transmittance using appropriate formulas.
The relationship between pore size and pressure follows the Washburn equation:
D = 4γCosθ / p
In this formula, D represents the pore diameter, γ is the surface tension of the liquid, θ is the contact angle, and p is the pressure difference.
Pore size distribution can be calculated using the following formula:
f(D) = -d[Fw/Fd × 100]/dD
Here, Fw is the flow rate of the wet sample, and Fd is the flow rate of the dry sample.
Pet Bottle Flake Pelletizing Line
High Capacity Pet Bottle Flake Pelletizing Line,Precision Pet Bottle Flake Pelletizing Line,Affordable Pet Bottle Flake Pelletizing Line,Customizable Pet Bottle Flake Pelletizing Line
Zhejiang IET Intelligent Equipment Manufacturing Co.,Ltd , https://www.ietmachinery.com
