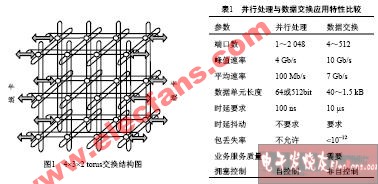
Direct interconnection structure (direct interconnection network, DIN) is a system composed of processing nodes interconnected in a certain way. The processing node in the direct interconnection structure is the service source, and at the same time it is the forwarding node. Fig. 1 is a torus direct interconnection structure. In the figure, circles represent processing nodes, also called switching nodes or routing units. DIN is widely used in large multiprocessor systems (mulTIprocessors), interconnection between multiple computers, and scalable shared cache multiprocessor systems. Its structure has high parallelism (parallelism) characteristics and excellent scalability. The data exchange application refers to technologies used in LAN or WAN, such as ATM technology, TCP / IP technology, etc. This paper applies DIN technology to data exchange to achieve a high-performance data exchange structure.
Table 1 lists the main performance indicators of the two applications. It can be seen that the data exchange requires higher throughput and requires service quality assurance, but the packet delay requirement is not high. The data exchange structure needs to have non-blocking characteristics, and the services output to different ports will not affect each other. It should be ensured that multiple concurrent services are transmitted at the requested bandwidth at the same time.
DIN has good scalability and distributed characteristics, but services between different ports greatly affect each other, resulting in low structural throughput. With the development of VLSI technology, larger buffers, higher clock frequencies and data transfer rates can be realized in hardware, making it possible to apply DIN to data exchange.
Literature [1] compares the difference in topological properties between the traditional data exchange structure and DIN, and gives an easily extensible data exchange structure. Literature [2] simulates and analyzes the performance comparison between a direct interconnection structure and several typical data exchange structures. In literature [3], a router structure applied to data exchange is implemented, and the trade-offs between routers are analyzed Program.
This article aims to analyze the throughput, delay, routing algorithm and deadlock resolution based on the DIN structure. Some methods that can be used when constructing a data exchange structure using a directly interconnected exchange structure are obtained.
Two important characteristics in DIN are throughput and latency. Throughput refers to the maximum data rate (usually bit / s) accepted by each input port. Delay refers to the total time required for a packet from the source to the target node. Throughput and delay are not only related to the topology, but also related to the routing algorithm, service source model and flow control strategy used. This paper mainly analyzes the ideal throughput and conflict-free delay. Ideal throughput means that the routing algorithm can fully balance the load on all paths from the source to the target, and the flow control can ensure that there is no idle period on the bottleneck channel. Conflict-free delay refers to the transmission time required for packets without internal blocking.
Application Analysis of Direct Interconnect Structure in Data Exchange
Screw Thread type NTC Temperature Sensor with the properties of liquid temperature measurement, good waterproof effect and plug-in detection has been used into water heater, liquid temperature measurement, testing water temperature in pipe and so on.
Temperature range is from -30°C to 150°C.
Screw Thread Sensor
Screw Thread Sensor,Water Temperature Sensor,Liquid Temperature Sensor
Feyvan Electronics Technology Co., Ltd. , http://www.fv-cable-assembly.com
