GIS, or Geographic Information System, is an advanced information system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. Unlike other information systems, GIS specializes in working with geographic data, making spatial analysis a core function of the system. This capability allows users to explore relationships, patterns, and trends that are not easily visible through traditional methods.
GIS can be interpreted in multiple ways: as a Geographic Information System, a Geographic Information Science, a Geographic Information Service, or even a Geographic Information Software. Each interpretation reflects different aspects of how GIS is used in research, application, and service delivery.
**Basic Functions of GIS Software**The core functions of GIS software typically include five main components: data input and verification, data storage and management, data transformation, data output and presentation, and user interface. These functions work together to ensure accurate and efficient handling of spatial data throughout the entire workflow.
**Data Entry and Inspection**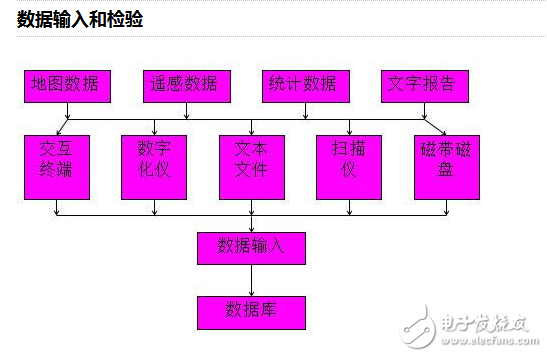
While some of the tools used for data entry may now be outdated, the fundamental principles remain the same. Data entry involves collecting geographic data from various sources, such as surveys, satellite imagery, or existing maps, and ensuring its accuracy before it is stored in the system.
**Data Storage and Management**Efficient data organization and management are crucial for the performance of any GIS system. In modern applications, common data products include 4D datasets: Digital Line Graphs (DLG), Digital Raster Graphics (DRG), Digital Elevation Models (DEM), and Digital Ortho Maps (DOM). These datasets form the backbone of many GIS projects and are essential for accurate spatial analysis.
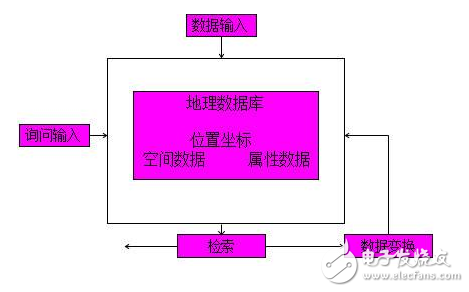
GIS software provides powerful tools for transforming spatial data. This includes both vector and raster operations, such as overlaying maps, performing buffer analysis, calculating distances, or analyzing terrain features. Through these transformations, users can gain deeper insights into geographic patterns and relationships.
**Data Output**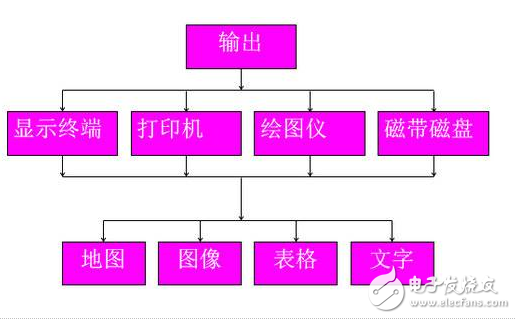
The user interface in a GIS system serves as the bridge between the user and the software. It enables interaction through menus, command languages, graphical interfaces, and even natural language processing. A well-designed interface ensures that users—whether experts or non-technical professionals—can efficiently navigate and utilize the system's capabilities.
**Classification of GIS Software by Function**Data Analysis Processing: This function involves analyzing spatial and attribute data to generate meaningful results. It includes operations like map overlay, spatial queries, and statistical analysis, which help in understanding geographic patterns and making informed decisions.
Data Storage and Management: This refers to how geographic data is organized, stored, and accessed within the system. Efficient database management ensures that spatial and attribute data are accurately linked and easily retrievable for further analysis.
Data Output Representation: The output module converts raw or processed data into visual formats such as maps, tables, charts, or graphs. This makes it easier for users to interpret and communicate the results of their analysis.
Data Input: This process involves acquiring and converting data from various sources, such as digitizing maps, scanning images, or importing remote sensing data. The method of input depends on the type of data and the equipment available.
There are generally three main methods of data input: manual digitization using a tracking tablet, raster digitization via scanning, and keyboard input for attribute data. Each method has its own advantages and is suited to different types of data and applications.
User Interface Module: This module is responsible for receiving user commands, programs, or data. It plays a vital role in enabling interaction between the user and the system, especially since many GIS users are not computer specialists. A good user interface enhances usability and makes the system more accessible to a wider audience.
I-type Inductance Core,I Inductor Model,Ring I-type Inductance,Design Of I-Shaped Inductor
Xuzhou Jiuli Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.xzjiulielectronic.com
