In short, GIS stands for Geographic Information System, which is an information system designed to manage and analyze spatial data. It relies on a database management system (DBMS) to organize and store geographic information. What sets GIS apart from other systems is its ability to perform spatial analysis, using geographic data as the core of its operations.
GIS can also be interpreted in different ways:
- Geographic Information System
- Geographic Information Science
- Geographic Information Service
- Geographic Information Software
**Basic Functions of GIS Software**The fundamental functions of GIS software typically include five key components: data input and verification, data storage and management, data transformation, data output and presentation, and user interface design.
**Data Input and Inspection**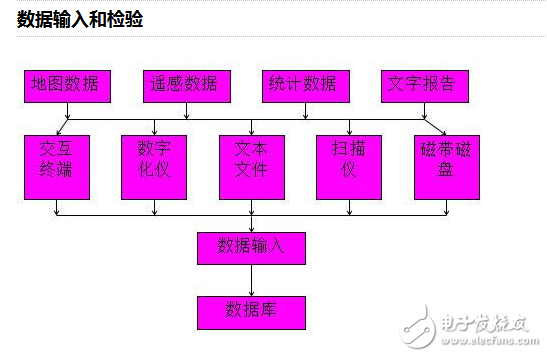
Although some of the hardware may have become outdated, the overall concept remains relevant today.
**Data Storage and Management**Proper organization and management of geographic data are crucial for effective GIS performance. Common data types used in GIS include 4D products such as Digital Line Graphs (DLG), Digital Raster Graphics (DRG), Digital Elevation Models (DEM), and Digital Ortho Maps (DOM).
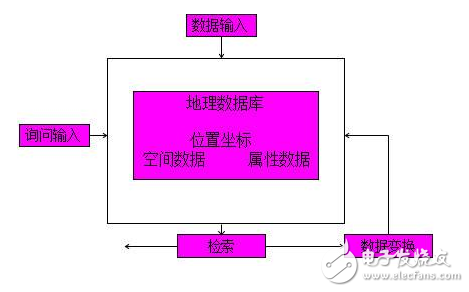
This function enables comprehensive analysis of both spatial and attribute data. It supports vector-based operations like overlays, buffers, and terrain analysis, as well as raster-based operations such as arithmetic calculations, logical processing, and clustering. These tools help in making full use of spatial data for decision-making and planning.
**Data Output**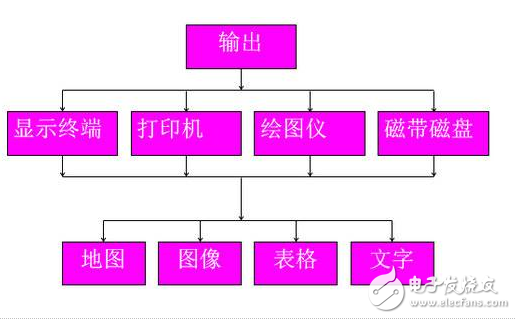
The user interface serves as the bridge between the user and the system. It includes tools like menus, command interpreters, natural language processing, and graphical interfaces that make it easier for users to interact with the system. The program and data interfaces also allow users to connect their own modules and use non-standard data formats.
**Classification of GIS Software by Function**Data Analysis and Processing:
This involves analyzing one or more maps and their associated attributes. It generates new outputs based on existing data, such as overlaying maps or performing spatial measurements. Spatial functions can be point-based, region-based, or neighborhood-based, including tasks like area calculation, path finding, and image classification.
Data Storage and Management:
It deals with organizing geographic elements—points, lines, and polygons—and their relationships. This process uses database management systems (DBMS) to store and manipulate data efficiently through operations like querying, extracting, and converting data formats.
Data Output and Representation:
This module presents data in a user-friendly format, such as maps, tables, charts, or graphs. Outputs can be displayed on screens, printed, or stored digitally. It ensures that the data is presented clearly and effectively for decision-making purposes.
Data Input Methods:
There are three common methods for data input:
1. Handheld digitizers: Used for manually tracing points and lines on maps.
2. Scanners: Convert images into grid data for raster analysis.
3. Keyboard input: Enters attribute data such as codes and symbols after being encoded.
User Interface Module:
This module allows users to interact with the system through menus, commands, and graphical interfaces. It simplifies complex tasks for non-expert users and enhances the usability of GIS systems. It also provides real-time help and guidance, making GIS a more accessible and interactive tool for professionals and students alike.
Ring Common Mode Inductor,UU Common Mode Inductor,Vertical Plug-in Common Mode Inductor,Power Line Common Mode Choke
Xuzhou Jiuli Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.xzjiulielectronic.com
