What do the different colored wires represent? Today, Xiaobian is here to guide you through the meanings behind these colorful cables!

Understanding wire colors is essential for safe and effective electrical work. Here’s a breakdown of common color codes:
1. **Black** – Often used for internal wiring in devices and equipment.
2. **Brown** – Typically represents the positive terminal in DC circuits.
3. **Red** – Used for Phase C in three-phase systems; also serves as the collector in transistors or the cathode in diodes and thyristors.
4. **Yellow** – Indicates Phase A in three-phase systems; also acts as the base in transistors or the control terminal in thyristors and triacs.
5. **Green** – Usually represents Phase B in three-phase systems.
6. **Blue** – Commonly used for the negative terminal in DC circuits, or the emitter in transistors and the anode in diodes and thyristors.
7. **Light Blue** – Refers to the neutral or grounding neutral line in three-phase systems.
8. **White** – Often used as the main electrode in bidirectional thyristors or for general use when no specific color is defined.
9. **Yellow and Green Striped** – This combination is used for safety ground wires, helping to identify the protective earth connection.
10. **Red and Black (Parallel)** – Used in AC circuits with dual-core or stranded wires.
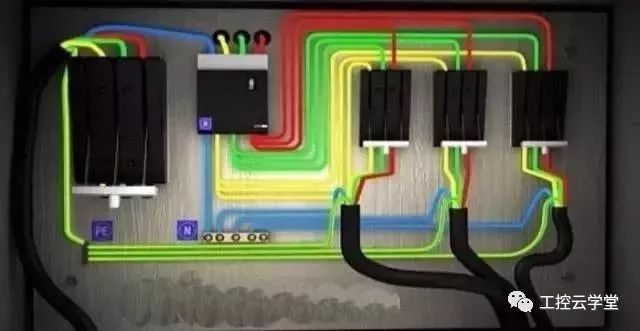
When choosing wire colors based on the circuit, it's important to follow standard guidelines:
- In **AC three-phase systems**, Phase A is yellow, Phase B is green, Phase C is red, the neutral is light blue, and the ground is yellow-green.
- For **double-core AC circuits**, red and black are typically used together.
- In **DC circuits**, brown is the positive, blue is the negative, and light blue is the grounded neutral.
- In **semiconductor circuits**, red is the collector, yellow is the base, and blue is the emitter. The anode is blue, while the cathode is red for diodes and thyristors. The control electrode is yellow, and the main electrode is white in bidirectional thyristors.
- Internal wiring in devices is usually black, while semiconductor circuits may use white. If there is confusion, other colors like orange, purple, gray, or pink can be used as alternatives.
It’s also important to note that if a wire has multiple color-coded sections, the colors should be chosen based on the function they need to represent in the circuit.
Here is a summary of the national standards for three-phase wire colors:
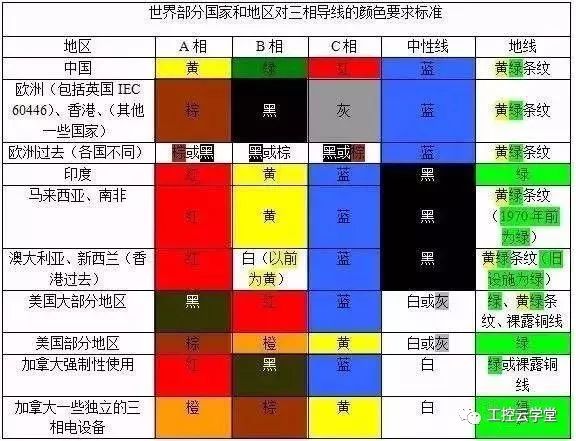
By understanding these color codes, you can ensure safer and more efficient electrical installations. Whether you're working on a simple device or a complex system, knowing what each color means is crucial.
PP Self Closing Wrap is braided of environmentally freindly PP yarn ,it light weight ,flame resistance,abrasion resistance,and heat insulation,it easy wrap around design and the extra overlap to enclose around important wires in eletronic communication and power system.
Applications :
PP woven wrap/Velcro/ zipper sleeve is widely used in the field of protecting cables,wiring harnesses and tubes. Such as: automobile wire harnesses ,electronic device ,rail way.
PP Self-Wrapping Sleeve,PP Self Closing Wrap,PP Split Sleeving,PP Self Closing Sleeve
Dongguan Liansi Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.liansisleeve.com
