With the continuous development of the internet era, the web has become a fundamental infrastructure for information exchange. Increasing numbers of devices now require internet connectivity, especially in embedded systems such as PDAs, where wireless communication is essential. One common method for household appliances to achieve smart functionality is through dial-up internet access. Among various network connection methods, dialing into an ISP via a traditional phone line remains one of the most cost-effective and practical solutions. The primary data link layer protocol used in this process is the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP).
This paper explores the PPP negotiation process involved in dial-up internet access, delves into the design of a network dialing program, and validates its implementation on an embedded platform based on the ARM9 processor.
**1 System Hardware Platform Construction**
The system utilizes the S3C2410X chip, which is built around the ARM920T core. This 32-bit RISC-based microprocessor is specifically designed for handheld devices and applications that demand low power consumption and cost efficiency.
For wireless communication, a GPRS module is employed. The Wavecom Q2403A is a versatile wireless modem that operates over GPRS networks, supporting voice calls, SMS, and data transmission. It offers multiple interfaces, including power connectors, LCD, SIM card, charging, headphone, and microphone ports, along with various peripheral interfaces for specialized functions. When transmitting data via GPRS, the Q2403A achieves download speeds of up to 26.8 Kb/s and upload speeds of 13.4 Kb/s. The hardware architecture of the system based on the ARM processor is illustrated in Figure 1.
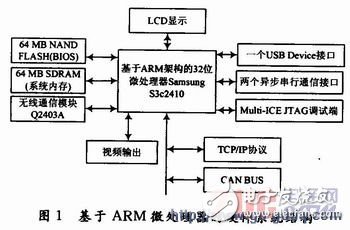
**2 Network Dial-Up Connection Process**
This article uses GPRS as an example to explain the detailed steps involved in establishing a network dial-up connection. The process involves using the PPP protocol to create a connection and leveraging GPRS for data transfer. The PPP link establishment consists of three main stages: link creation, authentication, and network negotiation.
(1) **Establishing the PPP Link**
The Link Control Protocol (LCP) is responsible for setting up the communication link. During this phase, the basic communication parameters are negotiated and selected.
(2) **User Authentication**
In this stage, the client sends its credentials to the remote access server. A secure authentication method is applied to prevent unauthorized access or impersonation. Until the authentication is successfully completed, the process cannot proceed to the next phase. If the authentication fails, the system moves to the link termination phase.
Commonly used authentication protocols include the Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) and the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP), which provide varying levels of security.
(3) **Negotiating the Network Layer Protocol**
Once the authentication is complete, the Network Control Protocol (NCP) is invoked. This protocol handles higher-level protocol issues over the PPP link. For instance, the Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) can assign dynamic IP addresses to users connecting via dial-up.
Through these three stages, a fully functional PPP connection is established, enabling reliable and secure internet access through dial-up methods.
Heat-shrinkable tubing is a special heat-shrinkable sleeve made of polyolefin. The outer layer is made of high-quality soft cross-linked polyolefin material and the inner layer of hot melt adhesive composite processing and become, the outer layer of material has the characteristics of insulation, corrosion and abrasion resistance, etc., and the inner layer has the advantages of low melting point, waterproof sealing and high adhesive properties.
Heat-shrink tube,Heat shrinkable tubing,thermal contraction pipe,Shrink tube
Mianyang Dongyao New Material Co. , https://www.mydyxc.com
