1 Concept of Internet of Things
The concept of the Internet of Things (Intemet of things) was proposed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1999. At present, there is no uniform and precise definition in the industry. The early Internet of Things was a logistics network that relied on radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. With the development of technology and applications, the connotation of the Internet of Things has changed significantly. In the new era, the Internet of Things refers to the deployment of embedded chips and software with certain sensing capabilities, computing capabilities and execution capabilities in entities in the physical world, making them "smart objects", and achieving information transmission, coordination and Processing, so as to realize the interconnection between things and things, and people. Connect all items to the Internet through information sensing equipment such as radio frequency identification to achieve intelligent identification and management.
Another term in the field of perception is the sensor network, which combines a large number of various types of sensor nodes (sensing, collecting, processing, sending and receiving, and network) into an autonomous network to realize dynamic collaborative sensing of the physical world. It can be seen that the sensor network is an internet of things for the purpose of perception. From the perspective of users or industrial applications, it is also called the Internet of Things, so the concepts of the sensor network and the Internet of Things are essentially the same. There are some differences in the usage scenarios of the two concepts. The sensor network is an important means and infrastructure to realize the communication of things. Therefore, it is more to describe the network itself from the perspective of implementation. The Internet of Things describes the network of things and things from the perspective of application. In this article, according to the actual situation, both concepts will be used.
The clear development of the Internet of Things has a history of 5 years. Japan first proposed the U-Japan concept with the goal of developing an ubiquitous network society in 2004. It plans to invest a total of US $ 2.9 billion from 2O04 to 2007. It is expected that it will bring in 2010 Direct income of $ 37.1 billion. South Korea has proposed the U.Korea strategy and the IT839 strategy. It plans to invest a total of 70 billion US dollars by 2010. The development of the Internet of Things is one of the three major infrastructures. In April 2009, the US government announced a $ 4 billion smart grid investment plan. Based on the existing power grid, the smart grid is implemented by introducing advanced sensing and measurement technologies, control methods, and decision support systems in all aspects of power generation and transmission. The power grid is highly reliable and efficient. The smart grid can achieve the goals of high-voltage transmission line safety monitoring, power equipment working condition monitoring, intelligent user demand response, real-time pricing, power outage detection, and power quality monitoring. The US Department of Energy expects this plan to save $ 80 billion in investment over the next 20 years.
2 Key technologies of the Internet of Things
Several key links of the Internet of Things can be summarized as "awareness, transmission, processing", to achieve "timely, accurate and comprehensive acquisition and processing of information, to achieve scientific decision-making, reduce costs, improve efficiency, protect the environment, enhance security and other goals, more Conducive to the sustainable development of mankind. " Among them, sensor technology, nanotechnology, embedded intelligent technology, radio frequency identification technology, and network and communication technology provide the foundation for the development and wide application of the Internet of Things.
(1) Sensor and sensor node technology
The sensor refers to a device or device that can sense a predetermined measured index and convert it into a usable signal according to a certain rule, and usually consists of a sensitive element and a conversion element. There are various types of sensors, which can be classified according to usage, material, output signal type, manufacturing process, etc. Common sensors include speed sensors, thermal sensors, pressure and force sensors, position sensors, liquid level sensors, energy consumption sensors, acceleration sensors, radiation sensors, vibration sensors, humidity sensors, magnetic sensors, gas sensors, etc. . With the development of technology, new types of sensors are constantly being produced. The application fields of sensors are very wide, including industrial production automation, national defense modernization, aviation technology, aerospace technology, energy development, environmental protection and biological sciences.
With the application of nanotechnology and microelectromechanical system (MEMS) technology. The reduction of sensor size and the improvement of accuracy have also greatly expanded the application field of sensors. The sensor nodes in the Internet of Things are composed of data collection, data processing, data transmission and power supply. Nodes have perception capabilities, computing capabilities, and communication capabilities. That is, based on traditional sensors, they add collaboration, computing, and communication functions to form sensor nodes. Intelligentization is one of the important development trends of sensors. Embedded intelligence technology is an important means to realize the intelligence of sensors. It is characterized by combining hardware and software, using the low power consumption, small size and integration of embedded microprocessors. The advantages of high and embedded software such as high efficiency and high reliability, combined with artificial intelligence technology, promote the realization of the intelligent environment in the Internet of Things.
(2) Radio frequency identification technology
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically identifies target objects and obtains relevant data through radio frequency signals. RFID attaches electronic tags to objects to achieve efficient and flexible management, which is one of the supporting technologies of the Internet of Things. A typical RFID system consists of electronic tags, readers and information processing systems. When an item with an electronic tag passes a specific information reader, the tag is activated by the reader and transmits the information carried in the tag to the reader and the information processing system through radio waves to complete the automatic collection of information. The information processing system undertakes the corresponding information control and processing according to the demand.
(3) Network and communication technology
The sensor network relies on network and communication technology to realize the transmission and coordination of sensory information. The network technology of the sensor network is divided into two categories: near field communication and wide area network communication technology. In terms of wide area network communication, IP Internet, 2G / 3G mobile communication, satellite communication technology, etc. have realized the remote transmission of information. In particular, the development of the next-generation Internet with IPv6 as the core will create the possibility of assigning IP addresses to each sensor, and also create good basic network conditions for the development of the sensor network. The representative short-range communication technology is the current mainstream technology. The 805.15.4 specification is a physical layer and media access control layer specification for low-speed close-range communication developed by IEEE. It works in the Industrial Scientific Medical (ISM) band and is license-free The 2.4 GHz ISM band can be used worldwide. 802.15.4's low power consumption, low rate and short-distance transmission characteristics make it very suitable for supporting simple devices with limited computing and storage capabilities.
With the further expansion of the Internet, the industry has begun to study how to extend the use of IP to resource-constrained sensor node devices through a new type of low-power network connection technology. The IETF 6LowPAN working group is responsible for the Iev6over 802.15.4 protocol, An adaptation layer is added between the application layer and the MAC layer, so that IPv6 can achieve efficient communication on the 802.15.4 network, thereby gradually achieving the integration of the Internet of Things and the Internet. At present, IETF has formed two RFCs in this field: RFC 4919 and RFC 4944. The Internet of Things can integrate the functions of all the above technologies. Realize a fully interactive and reactive network environment.
3 Integration requirements and architecture of the Internet of Things and telecommunications networks
The sensor network south is composed of a large number of micro-sensor nodes deployed in the observation area. It mainly forms a multi-hop self-organizing network system through wireless communication. The purpose is to cooperatively sense, collect information of the sensing objects in the network coverage area, and transmit it to the observer. . The typical sensor network structure is shown in Figure 1. It consists of sensor nodes and sink nodes. The sensor nodes form a network through self-organization, and the nodes communicate with each other wirelessly. The multi-hop method transmits the sensed data to the gateway node. The gateway node uses long-distance communication to transmit the regional data to the remote application center. . Due to the large number of nodes in the sensor network and the large amount of data collected, the data usually requires collaborative processing and fusion between nodes.
At present, most sensor network applications are only isolated application systems, and there is no correlation and interaction with each other. To truly achieve the ultimate goal set by the Internet of Things, it is necessary to achieve integration with the telecommunications network, break this isolated form, and form a new generation of Internet of Things. As the work done by the IETF 6LowPAN working group, the integration of sensors and IP Internet is an inevitable trend, that is, sensors will gradually become IP, and the scope of the Internet will gradually expand from traditional terminals such as personal computers to sensor nodes Will truly become a terminal node in the telecommunications network.
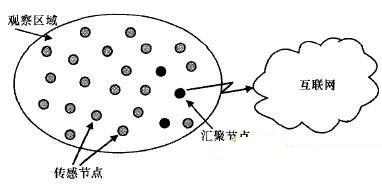
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of sensor network communication
Line Array Speakers,Linear Array Loudspeakers,Active Linear Array Sound Bar,Sound Linear Array Loudspeakers
The ASI Audio Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.asi-sound.com
