Foreword
In recent years, multi-function applications such as adding cameras, GPS, mobile TV broadcasting, and NFC to mobile phones have attracted attention. At the same time, with the rise of high-end devices equipped with high-performance application processors such as smartphones and tablet devices, in addition to today's call features, it also adds comfort, fast browser, streaming media, data access, cloud-ready functions, not only It is a brand new service for navigation, and high-quality communication functions have become an essential element.
As a function jointly sought by these mobile terminals, we will exemplify the correspondence of various networks. The mainstream of mobile communication specifications to date is still a 2G system called GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications). The 3G system UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System), which is equipped with higher quality and faster data transmission than GSM, is now common. Recently, some major countries have begun services for this next-generation communication specification called LTE (Long-Term Revolution), and wireless can also perform high-speed data communication like wired.
A typical portable terminal usually cannot communicate data during a voice call. SVLTE (Synchronous Voice and LTE) communication services that can also perform data communication when voice calls are prevalent in North America. In addition, in China, GSM is used for voice services, and TD-LTE (TDD system LTE) for data communication. Both of these simultaneous SGLTE (Synchronous GSM and LTE) communication services are also planned, IC manufacturers and The correspondence of the assembly manufacturers has also been carried out quickly.
TDD and TD-LTE
The TDD (Time Division Duplex) refers to a method in which radio waves of the same frequency are used for the uplink and downlink lines by one of the communication methods of the base station and the mobile terminal in both directions. In contrast, the way in which the upstream and downstream lines use different frequency waves is called FDD (Frequency Division Duplex).
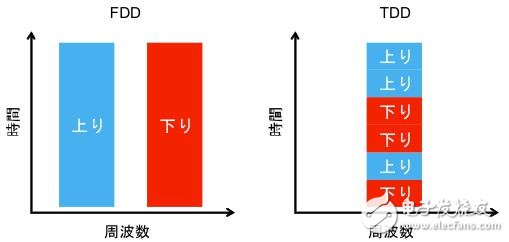
Figure 1: Comparison of TDD and FDD
LTE is the communication specification for mobile phones. This specification was certified by the standard 3GPP organization (3rd Generation Partnership Project) in March 2009. It is an intermediate technology between UMTS (3rd generation mobile phone) and the future 4G (4th generation mobile phone). At that time, it was called 3.9G. It was renamed 4G because it was approved by the ITU (International Telecommunication Union). Name it like this.
In general, in most cases, FDD-LTE using FDD is called LTE, not FDD-LTE, which is distinguished from LTE, which is called TD-LTE, which uses TDD. TD-LTE can transmit and receive at the same frequency. It can be said that the frequency configuration is relatively simpler than FDD-LTE. TD-LTE basically has the same technical difference as FDD-LTE except for the difference between FDD and TDD. It uses the same frequency band as 3G, and can be bandwidth width 1.4, 3, 5, 10 according to different situations. 15, 20MHz choose to use. LTE only supports packet communication. Voice communication is supported by VoIP technology called VoLTE. Generally speaking, it mainly supports data communication. It takes time to truly popularize voice services. TD-LTE is a service project that China is actively promoting. Japan has also begun to use 2.5GHz bandwidth for services. North America is also planning, and it is obvious that it will become popular all over the world.
TD-LTE RF circuit
As shown in FIG. 2, it is a circuit diagram of TD-LTE (SGLTE).
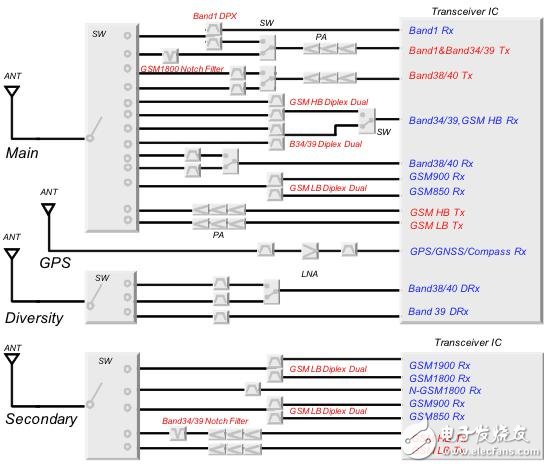
Figure 2: Circuit diagram of TD-LTE (SGLTE corresponding)
In the current TD-LTE corresponding terminal, in order to correspond to voice calls, triple mode and dual mode GSM and UMTS are indispensable. GSM has foreseen the problem of overseas roaming. Therefore, it can generally correspond to four different frequency bands of 850MHz, 900MHz, 1800MHz, and 1900MHz, and each of the frequency bands on the receiving side is equipped with filters one by one. The band1 of UMTS is FDD, so a duplexer (antenna duplexer) is required.
In China, the frequency bands for TD-LTE are classified into Band38, Band39, and Band40 according to 3GPP. Since it is a TDD system and does not require a duplexer, the transmission side has a filter corresponding to high power, and two credit filters are used on the main circuit side. The LTE system corresponds to the MIMO technology, and since it is a multi-antenna structure, a plurality of circuit sides are equipped with a credit filter.
Electrical secondary equipment refers to the low-voltage electrical equipment required for monitoring, controlling, regulating and protecting the work of primary equipment and providing operation conditions or production command signals for operation and maintenance personnel. Such as fuse, control switch, relay, control cable, instrument, signal equipment, automatic device, etc.
Intelligent Secondary Equipment
Intelligent Secondary Equipments,Power Equipments,Portable Switchgear,Park Switchgear
Shandong Shunkai electrical equipment co., LTD. , https://www.chinasdsk.com
