When we downloaded a program for the OMRON PLC (model: SYSMAC C200HG CPU43), a "memory error" occurred, as shown in the following image:
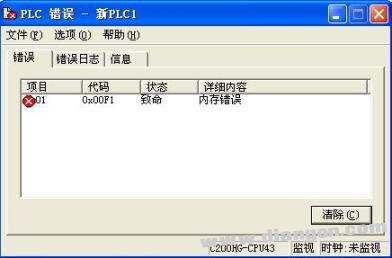
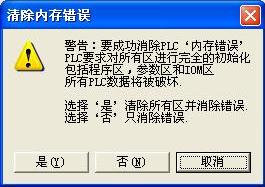
At this point, clicking the "Clear" button in the lower right corner will bring up a "Clear Memory Error" dialog box, as shown below. It's important not to click the "Yes" button blindly, because doing so will not only clear the error but also erase all data stored in the PLC memory. This can lead to the loss of all previously set parameters.
For example, in our system, the PLC controls a servo positioning module called NC112, and all control parameters for NC112 are stored in the DM area of the PLC. If you select "Yes," all those settings will be erased. If you had previously recorded the parameters, it’s manageable. However, if you didn’t, it could be a major issue—requiring you to reconfigure everything from scratch.
So, what causes a "memory error" in an OMRON PLC? There are several common reasons: ★ Incorrect PC configuration; ★ Errors in the program instructions; ★ The storage box is not installed, but the No. 2 DIP switch on the CPU is turned ON (meaning the program was transferred to the CPU without a storage box); ★ The storage box is installed, and the No. 2 DIP switch is also ON, but the memory is protected or contains code with verification errors.
To identify the exact cause, you can check the status bits of registers SR27211 through SR27215, as shown in the table below:
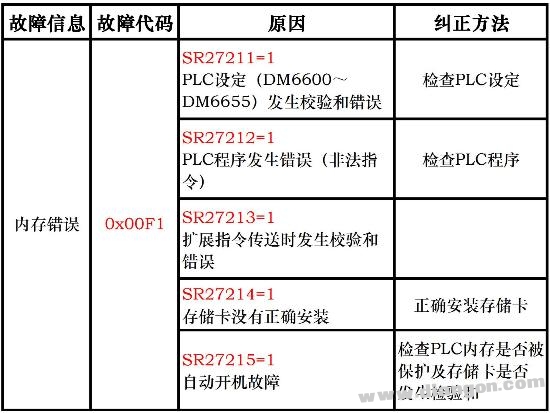
In conclusion, when dealing with PLC faults, it's crucial to first understand the root cause before taking any action. Avoid relying solely on previous experience or assumptions, as this could lead to unnecessary complications and additional work down the line.
Directional antennas are a vital component in wireless communication systems, renowned for their ability to transmit and receive signals with a high degree of directionality. These antennas are designed to focus their radiation pattern in a specific direction, enhancing the signal strength in that direction while minimizing interference and noise in other directions. Directional antennas come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations, each tailored to meet specific communication requirements. In this article, we will delve into the classification and key features of directional antennas.
Classification of Directional Antennas
-
Beamwidth and Gain
- Narrow Beamwidth Antennas: These antennas have a narrow radiation pattern, resulting in a high gain in a specific direction. They are ideal for long-distance communication and applications requiring high directionality, such as satellite communication, point-to-point microwave links, and radar systems.
- Medium Beamwidth Antennas: Offering a balance between gain and coverage, medium beamwidth antennas are commonly used in cellular networks, Wi-Fi access points, and other applications where a balance of range and coverage area is crucial.
- Wide Beamwidth Antennas: With a wider radiation pattern, these antennas provide broader coverage but with lower gain. They are suitable for applications where wide-area coverage is essential, such as TV broadcasting, emergency communication systems, and some types of IoT networks.
-
Polarization
- Linearly Polarized Antennas: These antennas radiate energy with a linear polarization, either horizontally or vertically. They are commonly used in terrestrial communication systems due to their compatibility with most transmitting and receiving equipment.
- Circularly Polarized Antennas: Circular polarization occurs when the electric field vector rotates in a circular or elliptical path as the wave propagates. Circularly polarized antennas are ideal for satellite communication and applications involving moving receivers, as they maintain signal integrity even when the antenna's orientation changes.
-
Array Configuration
- Yagi-Uda Antennas: A popular type of directional antenna, Yagi-Uda antennas consist of a driven element and multiple parasitic elements. They offer high gain and directionality, making them suitable for long-distance communication and television broadcasting.
- Parabolic Dish Antennas: As discussed earlier, parabolic dish antennas use a parabolic reflector to focus the radio waves into a narrow beam. They are commonly used in satellite communication and radar systems due to their high gain and excellent directivity.
- Panel Antennas: Sector panel antennas are flat, directional antennas designed to cover a specific sector of a circle. They are widely used in cellular networks, where multiple panel antennas are mounted on towers to provide coverage in various directions.
-
Frequency Range
- Directional antennas are available in a wide range of frequency bands, from low-frequency (LF) and medium-frequency (MF) bands used for broadcasting and marine communication to high-frequency (HF), very high-frequency (VHF), ultra-high-frequency (UHF), and microwave bands used in cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication.
Directional Antenna WiFi,Directional Antenna TV,Directional Antenna LTE,Directional Antenna Indoor,Directional Antenna Outerdoor
Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.yetnorson.com
